Using the Kubeflow Pipelines SDK
This guide provides examples that demonstrate how to use the Kubeflow Pipelines SDK.
Before you start
To follow the examples in this guide, you must have Kubeflow Pipelines SDK version 0.2.5 or higher installed. Use the following instructions to install the Kubeflow Pipelines SDK and check the SDK version.
- Install the Kubeflow Pipelines SDK
- Run the following command to check the version of the SDK
The response should be something like this:
pip list | grep kfpkfp 0.2.5 kfp-server-api 0.2.5
Examples
Use the following examples to learn more about the Kubeflow Pipelines SDK.
Example 1: Creating a pipeline and a pipeline version using the SDK
The following example demonstrates how to use the Kubeflow Pipelines SDK to create a pipeline and a pipeline version.
In this example, you:
- Use
kfp.Clientto create a pipeline from a local file. When the pipeline is created, a default pipeline version is automatically created. - Use
kfp.Clientto add a pipeline version to the pipeline that was created in the previous step.
import kfp
import os
host = <host>
pipeline_file_path = <path to pipeline file>
pipeline_name = <pipeline name>
pipeline_version_file_path = <path to pipeline version file>
pipeline_version_name = <pipeline version name>
client = kfp.Client(host)
pipeline_file = os.path.join(pipeline_file_path)
pipeline = client.pipeline_uploads.upload_pipeline(pipeline_file, name=pipeline_name)
pipeline_version_file = os.path.join(pipeline_version_file_path)
pipeline_version = client.pipeline_uploads.upload_pipeline_version(pipeline_version_file,
name=pipeline_version_name,
pipelineid=pipeline.id)
- host: Your Kubeflow Pipelines cluster’s host name.
- path to pipeline file: The path to the directory where your pipeline YAML is stored.
- pipeline name: Your pipeline’s file name.
- path to pipeline version file: The path to the directory where the new version of your pipeline YAML is stored.
- pipeline version name: Your pipeline version’s file name.
Note: Pipeline names need to be unique across your Kubeflow Pipelines cluster. Pipeline version names need to be unique within each pipeline.
Adding a version to an existing pipeline using the SDK
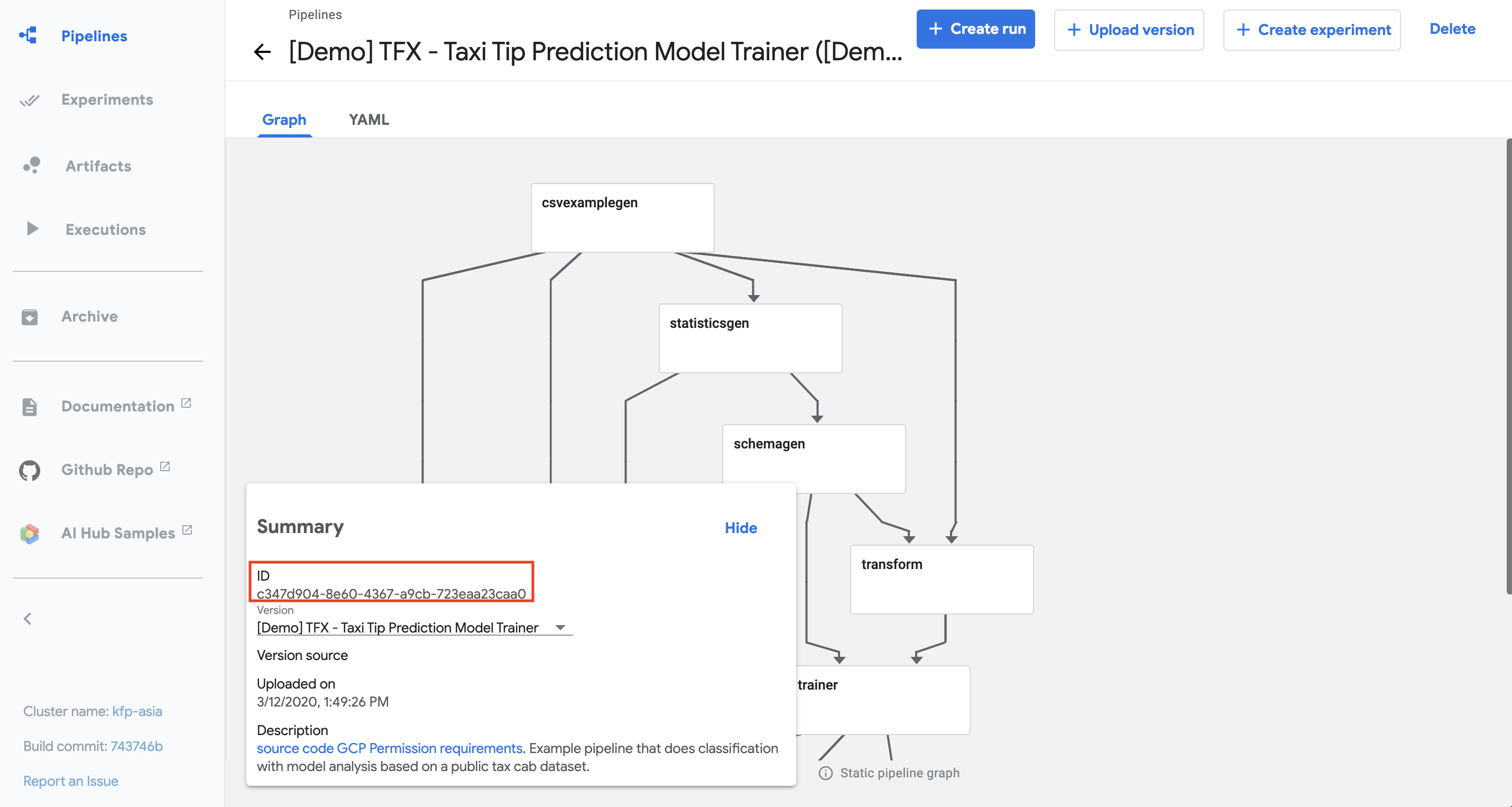
To add a pipeline version for an existing pipeline, you must find the
pipeline’s ID and use it with the upload_pipeline_version method. To
find a pipeline’s ID:
- Open the Kubeflow Pipelines UI. A list of your pipelines appears.
- Click the name of your pipeline. The pipeline details page appears.
- The pipeline ID is listed in the summary card, as shown below.
Example 2: Listing pipelines with a filter
The following example demonstrates how to use the Kubeflow Pipelines SDK to list pipelines with a particular pipeline name. If list_pipelines method is called without any input parameters, it will list all the pipelines. However, you can specify a filter as an input parameter to list pipelines with a particular name. Given that Kubeflow Pipelines requires pipeline names to be unique, listing pipelines with a particular name returns at most one pipeline.
import kfp
import json
# 'host' is your Kubeflow Pipelines API server's host address.
host = <host>
# 'pipeline_name' is the name of the pipeline you want to list.
pipeline_name = <pipeline name>
client = kfp.Client(host)
# To filter on pipeline name, you can use a predicate indicating that the pipeline
# name is equal to the given name.
# A predicate includes 'key', 'op' and 'string_value' fields.
# The 'key' specifies the property you want to apply the filter to. For example,
# if you want to filter on the pipeline name, then 'key' is set to 'name' as
# shown below.
# The 'op' specifies the operator used in a predicate. The operator can be
# EQUALS, NOT_EQUALS, GREATER_THAN, etc. The complete list is at [filter.proto](https://github.com/kubeflow/pipelines/blob/master/backend/api/filter.proto#L32)
# When using the operator in a string-typed predicate, you need to use the
# corresponding integer value of the enum. For Example, you can use the integer
# value 1 to indicate EQUALS as shown below.
# The 'string_value' specifies the value you want to filter with.
filter = json.dumps({'predicates': [{'key': 'name', 'op': 1, 'string_value': '{}'.format(pipeline_name)}]})
pipelines = client.pipelines.list_pipelines(filter=filter)
# The pipeline with the given pipeline_name, if exists, is in pipelines.pipelines[0].
Example 3: Creating a run using a pipeline version
Examine the run_service_api.ipynb notebook to learn more about creating a run using a pipeline version.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.